Greetings, dear reader! Today I propose to talk about one of the most popular fabrics - viscose. Why did she win the hearts of consumers so much? What kind of “pie” is this and what do you eat it with? Let's figure it out together.
1. History of the creation of viscose; 2. Technological process for the production of viscose; 3. What is viscose?; 4. Types of viscose fabrics; 5. Advantages and disadvantages of viscose fabric; 6. Use of viscose fabric; 7. Care of viscose; 8. Customer reviews.
History of the creation of viscose
The process of making viscose is progressive and lasted almost 50 years. The first description of the production of viscose fabric was made in 1844 by the Englishman J. Mercer, and the first to patent ready-made viscose fabric were the English chemists C.F. Cross and E. D. Bevan in 1893. They also gave the name to the fabric viscose, meaning “viscose”, since the raw material for production is a thick, viscous mass made from recycled wood cellulose. It is worth noting that the Russian chemist D.I. Mendeleev expressed respect for the new technology for obtaining raw materials and highly appreciated the merits of English scientists.
Protein threads
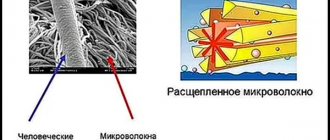
They consist mainly of biologically significant proteins of elongated shape. These include collagen - forms part of muscle, nervous, connective or other tissue in the human or animal body; and keratin - the main element of hair, skin and nails.
To understand what protein fibers are, you should indicate examples of them in the vertebrate body. So. Muscle fibers are long, cylindrical cells consisting of a bundle of myofibrils, fibers arranged in segments known as sarcomeres (the basic contractile units of striated muscles). Muscles come in different types: cardiac (forms the wall of the heart), smooth (found inside blood vessels) and skeletal. Nerve fibers are made up of axons. From small-diameter processes of nerve cells that conduct electrical impulses throughout the central nervous system.
Technological process for the production of viscose
Of course, since 1893, the process of producing viscose fabric has changed, and the technology has been modernized in many ways. Without going into depth, you can get viscose by describing four main stages:
- By crushing the wood into small chips and boiling it in an alkaline solution at high temperature, a base is obtained;
- By squeezing the mass through tiny holes in a special plate into a container with acid, threads are formed;
- Next comes the finishing stage;
- The final stage is drying.
Natural fibers
Natural fibers can be divided into three groups:
- vegetable;
- animals;
- mineral.
The most famous fibrous plant materials are cotton and flax. The finest cotton fibers cover the cotton seeds and are harvested by processing the seeds at cotton gins. Cotton fibers are thin-walled hollow tubes of varying thickness and length. Flax fiber is obtained from flax stems by soaking them and then processing them. Linen threads have a layered structure, they are stronger than cotton threads and are more hygroscopic.
Fibrous materials of animal origin are wool and silk. Wool threads are obtained from the hair of a variety of animals. Most often these are sheep and goats; they also use the wool of rabbits, camels, alpacas and others. Animal wool contains several types of crimped fibers - soft fluff, denser transitional hairs and hard awns. Natural silk fibers are a waste product of silkworms; they are extracted from the cocoons of silkworms. The length of the thread from one cocoon can reach 1 kilometer.
The most famous mineral fibrous material is asbestos, which is the finest flexible threads. It has high fire resistance and low electrical conductivity. However, asbestos dust is a highly carcinogenic substance and asbestos consumption in the world is rapidly declining.
What is viscose?
Very often people ask: “Is viscose a natural fabric or synthetic?” It's time to answer this question. But first, let me clarify that by artificial fiber we mean fiber that was created by man from artificial raw materials, but natural fiber is based on raw materials created by nature, for example, sheep wool or silkworm threads. As you already understood from the history of the origin of viscose, it is obtained from a natural product - wood, but using special chemical solutions, which is why there is a stable expression: “Viscose is an artificial product, but created on the basis of natural raw materials.”
Viscose appearance.
As practice shows, viscose may not consist of 100% wood cellulose, but may have various additives, both synthetic and natural. Therefore, the material directly depends on the composition. For example:
- 100% viscose . It is soft and delicate to the touch, but not durable;
- Viscose with elastane . This composition makes the fabric elastic;
- Viscose with polyester . Makes the fabric very durable;
- Viscose with cotton . This combination adds strength to the fabric, just like with polyester, but does not reduce its environmental qualities.
Depending on their origin, textile fibers are divided into natural and chemical
Brief information about textile fibersDepending on their origin, textile fibers are divided into natural and chemical.
Natural fibers, in turn, are divided into plant (cellulose), animal (protein) and mineral.
Plant fibers include cotton, flax, hemp, jute, etc.
Animal fibers include sheep and camel wool, llama and angora goat wool, and natural silk.
Mineral fibers include asbestos and glass fibers, the so-called metal threads.
Chemical textile fibers are produced by chemical processing of raw materials of different origins. These fibers are divided into artificial and synthetic.
Man-made fibers include:
fibers obtained by processing cellulose raw materials (wood, cotton and flax waste, etc.). These fibers are known as rayon, rayon and copper-ammonia. Artificial silk is used to make fabrics and knitwear;
fibers obtained by processing raw materials of animal or plant origin; these are so-called casein fibers, which are used for the production of knitwear;
staple fibers obtained from artificial fiber (viscose).
Synthetic fibers are obtained as a result of complex chemical processing of various organic substances. Depending on the origin and chemical composition, synthetic fibers are divided into the following subgroups:
polyamide: anid, kapron, vidlon, dederon, vetrelon, perlon, polan, stilon, nylon, rylan, etc.;
polyester: lavsan, grisuten, lanon, trevira, diolene, dacron, terylene, tergal, terital, etc.;
polyacrylonitrile: nitron, bulana, predan, volpril, dralon, dolan, redon, nikrylon, rolan, orlon, kurtel, kanekalon, etc.;
polyvinyl chloride: chlorin, rovil, fibrovil, isovil, luvil, beksan, evilon, etc.
Natural fiber fabrics
Cotton and linen fabrics
Cotton fabrics are soft and warm to the touch, especially when they are not starched (not finished), are easily torn, are hygroscopic and are especially suitable for making various lower and outer clothing, as well as bed linen.
The most suitable fabrics for bed linen are semi-linen fabrics. They are made from a mixture of linen and cotton.
Gray-white or gray-yellow linen fabrics become white after chemical bleaching. After natural bleaching, the grayish tint remains, but strength is not lost, as after chemical bleaching. Linen fabrics are cool to the touch, making clothes made from them especially pleasant to wear in hot weather. Linen fabrics are indispensable for making tablecloths, napkins, and towels.
Linen fabrics without any admixture of other fibers wrinkle easily. Therefore, synthetic or artificial fibers are added to the raw material.
Under the influence of water, cotton and linen fabrics swell, and the higher the water temperature, the more strongly. The swelling of the fibers explains the shrinkage of these fabrics, therefore, before sewing anything from them, they must be wetted and dried. Finished linen or cotton products should be dried without twisting after washing.
In weak solutions of baking soda (sodium bicarbonate), washing soda and potash (calcium carbonate), the swelling of cotton and linen fabrics increases, but their properties do not change. However, a concentrated solution of caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) destroys the fibers.
After treatment in soda solutions, the product must be washed several times and placed in a vinegar solution (200 g of vinegar per 10 liters of water).
Remember that sulfuric and nitric acids, even at room temperature, destroy cotton and linen fabrics.
Concentrated solutions of chlorine, hydrogen peroxide and other bleaches also have a harmful effect on fibers, especially at elevated temperatures. Therefore, solutions of these substances should be weak with a temperature of no more than 30 °C.
Alcohol, gasoline and other solvents do not have a harmful effect on cotton and linen fabrics.
With prolonged exposure to sunlight, cotton fabrics lose strength, and bleached fabrics lose strength more than unbleached fabrics. Linen fabrics are slightly affected by sunlight.
Wool fabrics
Wool fabrics are soft and elastic. Because wool is not thermally conductive, wool fabrics retain heat.
From wool of long-fiber varieties, so-called worsted yarn is obtained, from which durable worsted fabrics with a smooth surface are woven, especially suitable for outerwear for men and women. Short-fiber wool is used to produce hardware fabrics with a rough surface. They are used for men's outerwear. High-quality wool fabrics do not wrinkle. Wool-blend fabrics have become very widespread.
Wool fabrics are hygroscopic, but moisture does not reduce their strength.
Even a weak solution of caustic soda has a destructive effect on woolen fabrics. At room temperature (20 °C) or lower, a weak solution of washing soda does not have a harmful effect on woolen fabrics, but after treatment in such a solution they should be rinsed several times in clean water. Solutions of ammonia soda, ammonia water and neutral soap also do not have a harmful effect on woolen fabrics.
These tissues are destroyed by sulfuric, hydrochloric, nitric and even acetic acids; from the action of some bleaches they become hard and darken.
It is possible to treat woolen fabrics in a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide for 30-40 minutes at a temperature of 50-60 °C or in a cold solution for 4-5 hours.
From direct exposure to sunlight, woolen fabrics darken, become dry, light and brittle, and fade. They are also affected by mold. In addition, these fabrics should be protected from moths.
Silk fabrics
Silk is twice as strong as wool. Silk fabrics are very elastic and hygroscopic, but moisture does not reduce their strength. Not resistant enough to sunlight. Therefore, these fabrics are not suitable for curtains, blinds, beach ensembles, i.e. products exposed to sunlight.
Compared to other natural fibers, silk is resistant to various types of microorganisms.
Alkaline solutions (crystalline soda, bicarbonate of soda, caustic soda), acids and bleaches act on silk fabrics in the same way as on woolen fabrics. Even the weakest alkali solution reduces their shine.
Silk is not destroyed in alcohol, gasoline and other organic solvents.
Fabrics and knitwear made from artificial fibers
Viscose (svilose) and copper-ammonia silk
The viscose silk fabric is shiny and soft. Viscose silk is less durable than natural silk. It is used mainly for lining outerwear.
Copper-ammonia silk is pleasant to the touch and elastic. Its strength is approximately the same as the strength of viscose silk. It can be damaged by various molds, fungi and putrefactive bacteria. Used in the production of knitwear for underwear and outerwear.
The coarsest threads of copper-ammonia silk are used in the production of carpets.
Viscose and copper-ammonia silk swell significantly and lose strength when exposed to water.
Even weak solutions of washing soda have a harmful effect on artificial silk. Therefore, when washing such fabrics, it is most advisable to use an ammonia solution, solutions of borax, ammonia soda or neutral soap. The temperature should not be higher
After treatment in alkaline solutions, artificial silk fabrics must be thoroughly rinsed in a 3-5% solution of acetic acid.
Viscose and copper-ammonia silk are destroyed by the action of sulfuric, hydrochloric and nitric acids.
Bleach acts in the same way as on cotton and linen fabrics.
Compared to cotton fabrics, viscose and copper-ammonia silk are less resistant to sunlight.
Zellwolle
Cellwolle is a staple fiber (or fabrics made from it) that is obtained from viscose. It is used as an inferior substitute for natural wool and, accordingly, has similar properties.
Fabrics and knitwear made from synthetic fibers
Synthetic fibers are very durable compared to natural ones. The fabrics made from them do not wrinkle. They are non-hygroscopic, therefore the hygienic properties of linen made from 100% synthetic fibers are very low. When rubbed against skin and clothing, they become electrified and stick to the body. Fabrics made from synthetic fibers, except polyvinyl chloride, are not affected by organic solvents (alcohol, gasoline, etc.). They are not affected by insects and microorganisms.
Polyamide materials
Polyamide materials are smooth and cool to the touch. They are used to produce high-quality thin fabrics and knitwear, cords, ropes, etc.
Polyester materials
Polyester fibers are usually white and shiny, less often matte. Fabrics made from these fibers do not wrinkle. They are fluffy and soft to the touch. Insects and bacteria do not attack them. Polyester fibers (usually mixed with other textile fibers) are used to produce fabrics for women's dresses and suits, men's clothing, etc. They are also suitable for curtains (window glass does not transmit ultraviolet rays, which have a harmful effect on the strength of polyester fibers). Various other products are made from polyester materials: swimsuits, ties, scarves, summer shoes, etc. Threads from a mixture of natural and polyester fibers are used for the production of knitted products: women's and men's underwear, summer sweaters, suits, socks, etc. .
Polyacrylonitrile materials
Due to their valuable properties (bulk and fluffiness), polyacrylonitrile fibers are used for the production of knitwear and warm fabrics, from which blankets, bedspreads, military and sportswear, fabrics for upholstery, etc. are made. Fabrics made from a mixture of polyacrylonitrile and natural fibers are very durable.
Polyvinyl chloride materials
Polyvinyl chloride fibers are used primarily to produce technical fabrics and materials from which outerwear, underwear, fishing nets, etc. are made. However, these materials may shrink when washed in hot water or ironed. Due to the fact that polyvinyl chloride fibers are not thermally or electrically conductive, materials made from them are used to make antirheumatic products.
This type of underwear is known as “Vilan”.
How to recognize textile fibers
When purchasing textiles and knitwear or materials, do not rely only on their appearance. It is very important to know the composition and properties of the fibers of this material.
In order to correctly select the modes of washing, ironing, cleaning and other methods of processing textiles and knitted products, you must be able to recognize fibers.
To do this, it is usually enough to do a so-called combustion test: set fire to several threads of the material you are interested in.
Cotton and linen fibers burn relatively quickly; At the same time, the smell of burnt paper is felt. The ash obtained after combustion is gray-white in color.
Wool fibers burn more slowly than cotton and linen fibers; at the same time, the smell of burning horny substances, feathers and hair is felt. At the end of the burning thread, a charred, fragile ball is formed. The ash from the combustion of wool fibers is a black porous mass.
Rayon and copper-ammonia fibers burn slowly, leave little ash, and smell like burnt paper.
The casein fibers soften and melt, forming a ball that smells like a burning horny substance.
When exposed to high heat, synthetic fibers melt and stick together. When burned, they almost always form a very hard sintered ball.
If the result of the fiber combustion test is doubtful, a chemical examination of the fibers is carried out. It involves treating samples of material with various substances that can be purchased at a pharmacy or hardware store.
Using tweezers or a clothes clip, the sample is immersed in a glass with a hot solution of caustic soda (10 g of caustic soda per 100 g of water). Wool or natural silk dissolves in this solution without any residue. If a precipitate forms in the solution, then the fibers of the test sample are of plant origin (cotton or flax).
USEFUL TIPS FOR HOUSEKEEPING
Set as favorite
Bookmark
Email This
Hits: 8649
Types of viscose fabrics
Conventionally, viscose can be divided into three types: staple fiber, cord thread and viscose silk, and this division depends on the production method and the resulting qualities of the viscose fabric. Staple fiber is mainly used for sewing insulated clothing, blankets and carpets. Cord thread is used for high-quality fabric, and viscose silk is used for sewing bedding (pillowcases, sheets, duvet covers). Depending on the raw materials and the processing technology used, the following types of fabrics are distinguished:
- Tencel . This fabric originates from eucalyptus cellulose. Tencel feels silky and soft to the touch. Has a solid structure. It is used to make both casual clothing and bedding.
Appearance of Tencel fabric.
- Modal . Despite the fact that the fabric consists of 100% cellulose, it has all the qualities of cotton, so you can also sew clothes and bed linen from it. Such properties are achieved through weaving.
Appearance of modal fabric.
- Acetate . Acetate is made from cellulose waste. In appearance, this fabric resembles silk, but this is only in appearance. In fact, acetate is quite fragile, does not allow air to pass through well and practically does not absorb moisture. It is used for lining materials.
The appearance of the fabric is acetate.
- Cupra . The production of this material is not simple, it has its own technological features and difficulties, so it is one of the most valuable and high-quality. Cupra has good breathability, thermoregulation and durability, but it is difficult to care for. It makes great evening wear.
Appearance of cupra fabric.
- Siblon . The fabric is made from cellulose from coniferous trees. It is durable, hardly shrinks or wrinkles, is relatively cheap to produce, and is therefore widely used by consumers. It is mainly used for the production of textile fabrics.
Appearance of siblon fabric.
Differences between viscose, polyester and natural fabric
These three types have their differences:
- artificial wrinkles more than synthetics, but in both options the leather breathes well;
- polyester is electrified;
- When viscose burns, it emits a gas that smells similar to burning paper. After burning, ashes remain;
- burning of synthetics occurs with the smell of burnt plastic, after which only a solid piece of the former material remains;
- When burned, natural silk does not form a flame, but the smell of burnt hair appears.
Viscose and polyester
Advantages and disadvantages of viscose fabric
You already know that there are many varieties of viscose, but we will consider the characteristics of 100% viscose without the addition of other fibers. So, viscose has the following qualities:
- Does not cause allergies;
- Has pleasant tactile properties;
- Does not accumulate static electricity;
- Has high breathability and thermal conductivity;
- Holds color for a long time;
- Drapes beautifully.
Like all fabrics, viscose is also not without its drawbacks. For example, it has strong creaseability; viscose requires special care, because... If the material is not properly cared for, the products may become deformed and shrink, as well as become covered in pellets. Another important disadvantage is the wear period: viscose quickly loses its original appearance from ultraviolet rays. It is worth noting that manufacturers are struggling with the disadvantages presented above by adding other fibers.
Viscose and blended fabrics for sewing workwear
- Uniform shirts and overalls for medical workers, trade workers, bank employees, hotel staff, conductors and flight attendants are made from viscose shirting fabric with the addition of polyester.
- Viscose fabric is ideal for indoor service clothing. Shirts, skirts, and trousers made of mixed viscose fabric fit well, which is very important for the pleasant appearance of employees.
- Viscose fabrics are more elastic than natural ones, which allows for a better fit.
- Socks and underwear made of viscose fabric are comparable in quality to silk. In many companies, staff are recommended to wear viscose underwear, as it has antistatic properties and uniforms fit better on it.
- Uniform kimonos and “Asian” robes in chain restaurants stylized as Asian cuisine are made of viscose blend fabric.
Viscose care
I repeat that viscose requires special care, so if you want to preserve things for as long as possible without losing their appearance, you should bother:
- It is advisable to wash viscose products by hand, but if, due to certain circumstances, this is not possible, then use only the “delicate cycle” in machine wash.
- It is better not to wring out washed items too much, but to hang them semi-damp on the dryer and let the remaining water drain on its own, because... strong pressure during push-ups will negatively affect the shape of the product.
- After the water has drained, it is better to continue drying viscose items in a horizontal position for the same purpose, to avoid stretching and deformation.
- Under no circumstances should you iron things with an iron at high temperatures; use the minimum settings, or iron through wet gauze.
As you can see, in order to use viscose items in everyday life, you will need to face certain difficulties and inconveniences. But for the sake of a beautiful outfit, it may be worth being patient. In any case, the choice is always yours.
Basalt-plastic reinforcement
This is an interesting topic. Iron reinforcement in concrete, of course, for a long time had no equal in reliability and availability, but time passes, and the disadvantages that are inevitable when using iron, namely: its oxidation, followed by the destruction of what surrounds it, because that the volume of rust is always greater than the volume of the original iron, these disadvantages can be avoided if you use... stainless steel reinforcement made of composite materials , one of the components of which is basalt fiber.
But nothing is perfect, unfortunately, and the advantages of basalt-plastic reinforcement are accompanied by disadvantages that do not allow it to completely replace concrete reinforcement with metal.
Basalt-plastic reinforcement. Armplast Photos
Let me explain. The main disadvantage of basalt plastic is the lack of rigidity and elasticity. The consequence of this is that to achieve the strength of steel-reinforced concrete, it is necessary to use 4 times more basalt-plastic reinforcement.
The disadvantages also include the fact that basalt plastic binders significantly reduce the temperature at which such reinforcement loses its load-bearing properties.
The temperature limit of basalt is 1150 degrees, and the reinforcement made from it is only 300. Despite the fact that for steel the limit is 500 degrees. The problem will be solved when a more heat-resistant binder . (However, we understand that the concrete still needs to be heated somehow to 300 degrees so that the reinforcement in it loses its load-bearing properties, and this is difficult to achieve.)
By the way, without special additives, the plastic that is part of basalt reinforcement becomes brittle after a couple of decades of use, so it would be worth buying such reinforcement only from those manufacturers who can really be trusted.
On the other hand, there are advantages that are no less important. Basalt-plastic reinforcement is a dielectric. In this regard, it does not create any interference with electromagnetic radiation; stray currents and magnetic fields are not formed in it.
It is also worth mentioning that concrete and this reinforcement made of stone and resin have similar coefficients of thermal expansion , so all changes occur almost equally, and therefore no stress or damage occurs. (Steel, oddly enough, is also close to concrete in terms of thermal expansion.)
Yes, and unlike steel, basalt reinforcement has much lower heat transfer , so during the cold season, so-called “cold bridges” do not form in concrete.
Basalt reinforcement. Photo Construction Innovations
Before describing the production of basalt reinforcement, it is necessary to describe its structure and composition - it is these things that determine the manufacturing technology.
Basalt reinforcement is a bundle of basalt fibers (roving) bonded with plastic into a single rod. Another bundle of fibers is wound around this rod - this braided thread , it is similar to the protrusions on metal reinforcement and increases the adhesion between the reinforcement and concrete. The braided thread is also bonded with plastic and is firmly connected to the rod.
One of the options for the composition of the reinforcement is as follows:
- roving;
- resins;
- weaving thread;
- acetone;
- ethanol;
- Dicyandiamide.
Basalt roving. Photo Stone Age
Binders can be different types of resins:
- organosilicon;
- phenol-formaldehyde;
- epoxy;
- polyamide;
- polybenzimidazole;
- polybenzothiosole.
The technology for its curing depends on the resin used . But the production line for the production of basalt plastic is no different from the fiberglass production process shown in the video (only the roving changes):
In the video, you see how the supplied roving is impregnated with resin, then wrapped with braided yarn, and then passed through the resin curing equipment. The finished reinforcement is cut and packaged.
Basalt fiber for concrete
Concrete, of course, made our civilization. Just imagine how labor intensive the old way of building with stone or wood would have been. But still, concrete itself is far from perfect. The cement stone at its base does not have sufficient strength to withstand all the loads that arise during operation. In addition, no one is able to take into account all the loads. Therefore, thought moved in the direction of increasing the strength of concrete .
First they thought of adding metal shavings to the concrete. This is a good option, because dispersed particles are evenly distributed in the volume, taking on the load that previously went to the cement stone. But iron is iron, and its meeting with water ends predictably.
Basalt fiber 12 mm. Photo Geostyle
They also tried to add fiber to concrete, but this idea only became useful in our time. Fiber translated from Latin is “fiber”. Therefore, the composition may be different. This is true. The most popular options today are those with polypropylene and basalt fiber. Also still adding shavings and cut wire. And instead of basalt, fiberglass is sometimes used.
The first two are quite effective, as proven by the long-term use of fiber in road and capital construction for decades around the world. the principle : scattered particles, in this case fibers, take on the load from the concrete along tangents passing along the dividing line between the fiber and the cement. This occurs throughout the entire volume of the mixture, which distinguishes this load distribution from the distribution over a reinforcing frame made of metal rods.
The use of fiber allows you to partially or even completely abandon the use of metal reinforcement!
However, it is worth considering that the maximum benefit from the use of fiber will only be if you strictly follow existing technologies , use fiber of a specific length and thickness, in the proportion specified for a specific type of concrete.
The load-bearing capacity of concrete itself is directly dependent on the volume fraction of fiber in its composition. Over-reinforcement is just as bad as under-reinforcement.
Basalt fiber CemFibra R. Photo by Leroy Merlin
The shorter the fibers, the smaller the increase in strength.
In general, let's move on to comparing which is better: basalt or polypropylene fiber.
Basalt or polypropylene fiber - which is better?
Basalt fiber for concrete is chopped basalt roving (see above), the length of the fibers can be different, depending on the equipment settings. In general, they can be in the range from 1 to 150 mm.
Polypropylene fiber is a white polymer fiber with a length of 6 to 50 mm.
Now let’s compare the reference characteristics of both materials:
| Polypropylene fiber | Basalt fiber | |
| Compound | Polypropylene | Basalt |
| Fiber density, kg/m3 | 910 | 2800 |
| Melting point, °C | 160 | 1450 |
| Resistance to alkalis and corrosion | Low | High |
| Tensile strength, MPa | 150-200 | 450-600 |
| Modulus of elasticity, MPa | 4000-6000 | >100 000 |
is inferior to in all respects . What happens when you add both to concrete? In both cases, cracking is reduced, strength is increased, the number of microcracks is reduced, and, consequently, frost resistance and water resistance are increased. The depth of penetration of solutions from the outside is reduced from 20 to 2-3 mm.
However, we have seen test results that indicate that while strength increases with the addition of any fiber, greatest with the addition of basalt and metal fibers (the latter of which is bad in the long term).
| Type of fiber used | Fiber dosage, % by volume | Strength increase % |
| Basalt, length 12 mm | 0.1-0.25% by volume | 262 |
| Propylene, length 55 mm | 0.1-0.2% by volume | 111 |
| Amorphous metal, length 30 mm, steel, 54 mm | 0.1-2.0% by volume | 277 |
| Basalt 4, 6, 15 mm | 0-5% by volume | 210 |
This table clearly shows that propylene fiber has the lowest percentage increase in strength among those compared. Perhaps the popularity of this particular fiber is due to its low cost, the ability to add at any stage, and good mixing? But basalt fiber also has no problems with all of the above.
In general, the properties of basalt fiber are better than polypropylene, and the strength of concrete with it is higher.